Ever thought of the functions of the foreign exchange market and how they affect our daily lives?
The primary function of the foreign exchange market is to facilitate currency conversion. This market allows for the buying, selling, exchanging, and speculation of currencies. It operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, and currencies are traded in major financial centers across the globe.
The foreign exchange (forex) market is a global arena for exchanging different national currencies. It’s an expansive, decentralized network, a feature that sets it apart from markets like the stock exchange, which have central locations and formal exchanges. This decentralized nature means the forex market is influenced by a multitude of factors and players, rather than being controlled by a single authority.
In today’s interconnected global economy, understanding the foreign exchange (forex) market is crucial for business owners and professionals. The forex market is not just a platform for currency trading; it serves as a pivotal element in international trade and finance.
Learn more about foreign exchange in:
10 Factors that Influence Exchange Rates between Currencies
Exchange Rates and How they Affect Every Business
Major Players in the foreign exchange market
The forex market comprises a diverse set of participants, each playing a unique role.
- Governments and Central Banks
These entities are key players due to their potential to influence exchange rates through monetary policy, currency interventions, and other fiscal measures.
- Commercial Banks and Financial Institutions
They are the primary players, conducting the bulk of the transactions in the forex market. These institutions trade both on behalf of their clients and for their own accounts.
- Businesses and Corporations
Firms engaged in international trade need to convert currencies for transactions. They are a significant part of the market, managing currency risk through various forex instruments.
- Individuals and Retail Investors
From international travelers needing to exchange currencies to individual traders speculating on currency movements, these participants add to the market’s liquidity and dynamics.

So, what are the Key Functions of the Foreign Exchange Market?
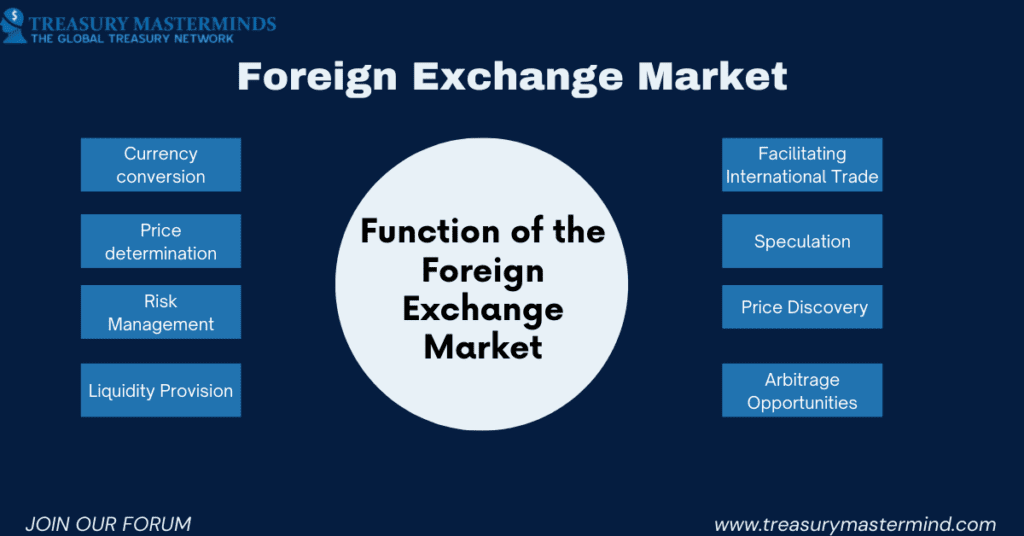
The foreign exchange market serves several crucial functions that are essential for businesses engaged in international trade. Here are key functions of the foreign exchange market:
1. Currency Conversion: The Cornerstone of Global Trade
This is one of the most important functions of the foreign exchange market. Imagine a German toymaker exporting goods to the United States. They sell $1 million worth of toys and need to receive payment in euros. This is where the forex market comes in. The toymaker can sell their US dollars and buy euros at the current exchange rate, ensuring they receive their earnings in their preferred currency.
But why not simply ask the buyer to pay in euros?
- Flexibility: Not all buyers can or want to pay in a foreign currency. The forex market offers flexibility for both parties.
- Efficiency: Exchange rates fluctuate constantly. The forex market provides access to competitive rates and swift execution of transactions, saving both buyers and sellers time and money.
- Risk Management: The forex market allows businesses to lock in exchange rates upfront through forward contracts, mitigating the risk of adverse currency movements impacting their profits.
2. Price Determination: The Dance of Supply and Demand
The forex market isn’t just a currency exchange booth; it’s a dynamic ecosystem where the price of each currency constantly fluctuates. This dance of supply and demand is influenced by various factors, like:
- Interest rates: Higher interest rates in a country can attract foreign investment, strengthening its currency.
- Economic performance: A strong economy with low inflation usually leads to a stronger currency.
- Political stability: Political turmoil or uncertainty can weaken a country’s currency.
- Speculation: Traders anticipating future currency movements can buy or sell currencies, impacting their prices.
3. Risk Management: Hedging Your Bets against Currency Swings
A sudden drop in the euro’s value against the yuan could significantly increase their import costs and hurt business profits. The forex market offers tools like forward contracts and options to hedge against such risks. By locking in an exchange rate upfront, businesses can protect themselves from adverse currency movements, ensuring predictable costs and safeguarding their profit margins.
4. Liquidity Provision: Ensuring Smooth Sailing in Currency Conversions
Imagine you’re trying to sell your vintage car collection in Japan but need to convert the Yen you receive back into euros. The forex market’s high liquidity comes in handy here. With billions of dollars traded daily, you can easily buy or sell any major currency without significantly impacting the exchange rate. This liquidity is crucial for businesses, as it ensures they can quickly convert currencies whenever needed without facing significant transaction costs.
5. Facilitating International Trade: Opening Doors to Global Markets
The forex market is the backbone of international trade. It allows businesses to:
- Import and export goods and services across borders.
- Invest in foreign companies and assets.
- Receive and make international payments.
- Without the forex market, international trade would be significantly more complex and expensive, hindering global economic growth and interconnectedness.
6. Speculation: The Thrill of the Chase
The forex market isn’t just for practical needs; it’s also a playground for speculators. These are traders who try to predict currency movements and profit from them by buying or selling currencies accordingly. While speculation can be risky, it adds to the market’s liquidity and can sometimes help correct imbalances in exchange rates.
7. Price Discovery: A Transparent Marketplace
The constant buying and selling of currencies in the forex market leads to transparent price discovery. This means that the exchange rates for different currencies accurately reflect the current economic conditions and market expectations. This transparency is crucial for businesses and investors, as it allows them to make informed decisions based on reliable information.
8. Arbitrage Opportunities: Keeping the Scales Balanced
Sometimes, there can be slight differences in the exchange rates for the same currency in different markets. Arbitrageurs exploit these discrepancies by buying a currency in the market where it’s cheaper and selling it in the market where it’s more expensive. This activity helps to maintain consistency in exchange rates across different financial centers.
By understanding the key functions of the foreign exchange market, you gain a deeper appreciation for the vital role the forex market plays in the global economy. It’s not just about buying and selling currencies; it’s about facilitating international trade, managing risk, and even providing opportunities for speculation. So, the next time you hear about the “FX market,” remember that it’s a complex and fascinating world with far-reaching implications for businesses and economies worldwide.
Join our Treasury Community
Treasury Masterminds is a community of professionals working in treasury management or those interested in learning more about various topics related to treasury management, including cash management, foreign exchange management, and payments. To register and connect with Treasury professionals, click [HERE] or fill out the form below to get more information.